The aerodynamic force is the resistance exerted by air on a moving vehicle. It’s the force felt by your hand when you put it outside your car window.
The main factors influencing the aerodynamic force are:
 Speed
Speed
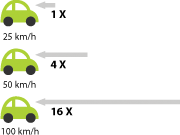
| Speed is the most significant factor influencing the aerodynamic force. It is directly proportional to the square of the speed, i.e. when you double your speed, the aerodynamic force quadruples. |
|
 |
 |
|
Since the relationship is exponential, going from 30 km/h to 40 km/h won’t have as much of an impact on the aerodynamic force as going from 100 km/h to 110 km/h. |
 The aerodynamic resistance coefficient
The aerodynamic resistance coefficient
 |
|
This resistance refers to the manner in which air circulates around the moving vehicle. It essentially relates to the shape of the vehicle. The presence of anything on the car body will increase this resistance. |
 |
Frontal area
|
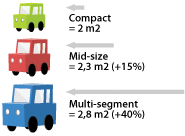
| To better understand what this represents, imagine a vehicle going through a foam wall. The frontal area would correspond to the surface of the hole in the wall. The larger the vehicle, the greater this factor. For example, the frontal area of a tractor trailer is much larger than that of a compact vehicle. |
|
 |
| How to reduce the aerodynamic force? |
Here are the main things you can do to better control the aerodynamic force and, thus, your fuel consumption.
1
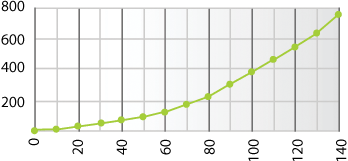
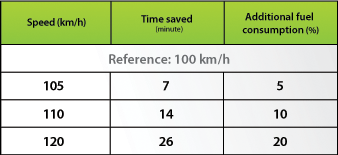
On the highway, reducing your speed will provide the greatest fuel savings. For example, as of 100 km/h, each additional km/h will cost you 1% more in fuel. The table below compares how long it takes to travel from Montreal to Québec City at different speeds and estimates fuel consumption differences.
Montreal-Québec City = 260 km
 |
|
For example, you can see that driving at a speed of 100 km/h versus 110 km/h provides fuel savings of 10% and only extends the travel time by 14 minutes. |
- To reduce your usual speed, gradually lower it. For example, start by going from 115 to 110 km/h and eventually lower this speed to 105 km/h. This will save you 1 full tank of gas in 10.
2
In addition to limiting the use of storage and bicycle racks as much as possible, it is best to remove these accessories immediately after use so as not to increase the aerodynamic resistance coefficient for too long, as this increases your fuel consumption.
3
Snow and ice obstruct air flow and increase the aerodynamic resistance coefficient, which increases your fuel consumption.
 Speed
Speed The aerodynamic resistance coefficient
The aerodynamic resistance coefficient